Intervals
INTERVAL data types allow us to conduct arithmetic calculations with temporal data types. Keyword DATE is casting operator. This operator is used so that Monetdb transform string to date data type.
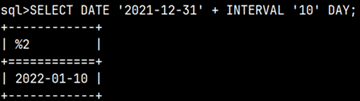 | SELECT DATE '2021-12-31' + INTERVAL '10' DAY; |
It is possible to subtract two dates or times. Result will be interval in seconds.
SELECT date '2020-09-28' | SELECT time '14:35:45' |
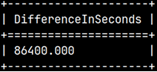 | 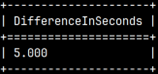 |
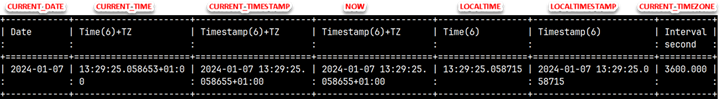
Current Date and Time
With these variables we can get information about current date, time and time zone (TZ).
SELECT CURRENT_DATE as "Date"
, CURRENT_TIME as "Time(6)+TZ"
, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP as "Timestamp(6)+TZ"
, NOW as "Timestamp(6)+TZ"
, LOCALTIME as "Time(6)"
, LOCALTIMESTAMP as "Timestamp(6)"
, CURRENT_TIMEZONE as "Interval second";
Transform Strings to Temporal Data Types
There are several ways how we can create temporal data types from the strings. If we have dates, times, or timestamps in ISO format then we can use casting operator, casting function or convert function.
SELECT DATE '1987-09-23' AS "Date"—————————————————– You can also use TIMETZ, TIMESTAMPTZ. | SELECT CAST('1987-09-23' as date) AS "Date" |
SELECT CONVERT('1987-09-23', DATE) AS "Date" | 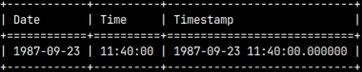 |
If string is not in temporal ISO format, then we have to use functions str_to_date, str_to_time or str_to_timestamp. These functions have second argument where we describe how to interpret string.
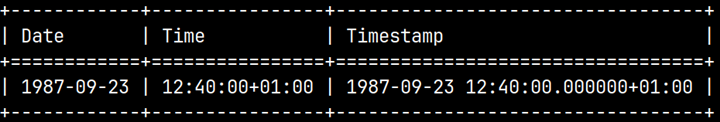
SELECT STR_TO_DATE('23-09-1987', '%d-%m-%Y') AS "Date"
, STR_TO_TIME('11:40', '%H:%M') AS "Time"
, STR_TO_TIMESTAMP('23-09-1987 11:40', '%d-%m-%Y %H:%M') AS "Timestamp";
All the specifiers used to describe dates and times can be found on the bottom of this page:
https://www.monetdb.org/documentation-Dec2023/user-guide/sql-functions/date-time-functions/
Here are just the major specifiers:
| %S | Seconds (00-59). | %u | Day of week (1-7). | %R | Time "15:36". |
| %M | Minutes (00-59). | %d | Day of month (01-31). | %T | Time "15:36:40". |
| %H | Hours (00-23). | %j | Day of year (001-366). | ||
| %m | Months (01-12). | %F | ISO 8601 format "2023-05-13". | ||
| %Y | Years "1981". | %V | Week of year (01-53). | %s | Seconds from 01.01.1970. |
| %z | "±hh:mm" timezone. | %Z | Name of timezone. |
Do it Reverse, Transform Dates and Times to Strings
Counterpart to functions above, are functions that transform temporal types to strings. Here we have functions DATE_TO_STR, TIME_TO_STR and TIMESTAMP_TO_STR. Again, we are using specifiers to describe how we want our string to look like.
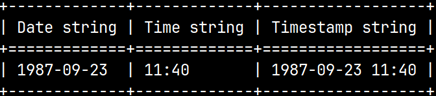
SELECT DATE_TO_STR( DATE '1987-09-23', '%Y-%m-%d') AS "Date string"
, TIME_TO_STR( TIME '11:40', '%H:%M') AS "Time string"
, TIMESTAMP_TO_STR( TIMESTAMP '1987-09-23 11:40', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M') AS "Timestamp string";
Extracting Parts of Times and Dates
It is possible to extract parts of temporal data types by using function EXTRACT.
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM CURRENT_DATE)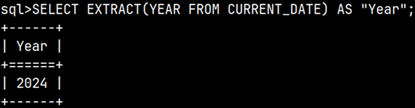
We can extract these parts:
| YEAR | QUARTER | MONTH | WEEK | DAY | HOUR | MINUTE | SECOND | DOY | DOW | CENTURY | DECADE |
It is also possible to use specialized functions to extract temporal parts. Some of these functions have double quotes around them.
| "second"(tm_or_ts) | "second"(timetz '15:35:02.002345+01:00') | 2,002345 |
| "minute"(tm_or_ts) | "minute"(timetz '15:35:02.002345+01:00') | 35 |
| "hour"(tm_or_ts) | "hour"(timetz '15:35:02.002345+01:00') | 16 |
| week(dt_or_ts) | week(date '2020-03-22') | 12 >ISO week< |
| "month"(dt_or_ts) | "month"(date '2020-07-22') | 7 |
| quarter(dt_or_ts) | quarter(date '2020-07-22') | 3 |
| "year"(dt_or_ts) | "year"(date '2020-03-22') | quarter(date '2020-07-22') |
| dayofmonth(dt_or_ts) | dayofmonth(date '2020-03-22') | 22 |
| dayofweek(dt_or_ts) | dayofweek(date '2020-03-22') | 7 >Sunday< |
| dayofyear(dt_or_ts) | dayofyear(date '2020-03-22') | 82 |
| century(dt) | century(date '2020-03-22') | 21 |
| decade(dt_or_ts) | decade(date '2027-03-22') | 202 |
This two functions can help to extract days or seconds from seconds interval.
| "day"(sec_interval) | "day"(interval '3.23' second * (24 * 60 * 60)) | 3 |
| "second"(sec_interval) | "second"(interval '24' second) | 24 |
Max and Min Date or Time
This is how we can find latest or earliest date or time.
| greatest(x, y) | greatest(date '2020-03-22', date '2020-03-25') | date '2020-03-25' |
| least(x, y) | least(time '15:15:15', time '16:16:16') | time '15:15:15' |
Difference Between Two Timestamps – timestampdiff functions
When subtracting two timestamps we can decide in which measure units to get the result.
| timestampdiff(ts_tstz, ts_tstz) | select timestampdiff(timestamp '2021-12-31 18:40:40', timestamp '2021-12-30 16:30:20') | interval '94220' second |
| timestampdiff_min(ts_dt_tz, ts_dt_tz) | select timestampdiff_min(timestamp '2021-12-31 18:40:40', timestamp '2021-12-31 16:30:20') | 730 |
| timestampdiff_sec(ts_dt_tz, ts_dt_tz) | select timestampdiff_sec(timestamp '2021-12-31 18:40:40', timestamp '2021-12-31 16:30:20') | 7820 |
| timestampdiff_hour(ts_dt_tz, ts_dt_tz) | select timestampdiff_hour(timestamp '2021-12-31 18:40:40', timestamp '2021-12-20 16:30:20') | 266 |
| timestampdiff_day(ts_dt_tz, ts_dt_tz) | select timestampdiff_day(timestamp '2021-12-31 18:40:40', timestamp '2021-12-20 16:30:20') | 11 |
| timestampdiff_week(ts_tm_tz, ts_tm_tz) | select timestampdiff_week(timestamp '2021-12-31 18:40:40', timestamp '2021-02-20 16:30:20') | 44 |
| timestampdiff_month(ts_tm_tz, ts_tm_tz) | select timestampdiff_month(timestamp '2021-12-31 18:40:40', timestamp '2021-02-20 16:30:20') | 10 |
| timestampdiff_quarter(ts_tm_tz, ts_tm_tz) | select timestampdiff_quarter(timestamp '2021-12-31 18:40:40', timestamp '2021-02-20 16:30:20') | 3 |
| timestampdiff_year(ts_tm_tz, ts_tm_tz) | select timestampdiff_year(timestamp '2021-12-31 18:40:40', timestamp '2024-02-20 16:30:20') | -3 |
Truncating Timestamp
This is great function that allows to round our Timestamp to 'millennium', 'century', 'decade', 'year', 'quarter', 'month', 'week', 'day', 'hour', 'minute', 'second', 'milliseconds' or 'microseconds'. In example bellow we rounded our timestamp to months. That is why all the values to the right side of the month are getting their minimal values.
| sys.date_trunc(field_str, timestamp) | sys.date_trunc('month', timestamp '2020-03-22 13:16:57.734639'); | timestamp '2020-03-01 00:00:00.000000' |
Unix Time
If we want to transform temporal data in and from Unix time, then we can use these two functions. One will transform number of seconds (counted from 01/01/1970, which is beginning of time) to regular timestamp. Second one will do the reverse. It will transform regular timestamp to seconds from the beginning of Unix time.
| sys.epoch(decimal(18,3) seconds) | sys.epoch(1234567890.456) | timestamptz '2009-02-14 01:31:30.456000+02:00' |
| epoch_ms(dt_or_tm_or_ts_or_interval) | epoch_ms(timestamp '2009-02-13 23:31:30.0') | 1234567890 |